EV Manuals PDF
EV History
Historically, the first EV car was created in 19th century by R. Anderson.
He tried to stay ahead of technology and built a car that's powered by electricity.
While competitors worked with minerals and successfully developed gasoline ICE.
In 1834, Thomas Davenport, who is considered the ancestor of the EVs.
Interest in electric transport was the fall in world prices for oil and gas, as well as the deterioration of the environment. Humanity began to think about alternative energy sources.
The announcement at the end of the 90s became a significant shift from the dead center. a new hybrid car Toyota Prius. People have rekindled interest in EVs.
And already decades later, a completely unique electric cars from Tesla Motors, led by Elon Musk, was born. More affordable models began to appear on the market, for example, the Nissan LEAF.
It will take more than one decade to fully switch to the use of EVs.
Developments to increase battery capacity and cruising range only prove that with the help of an electric car we can easily travel a lot hundreds of kilometers.
Types of Electrified Vehicles
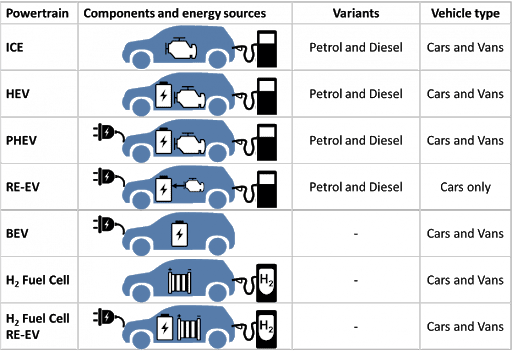
ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) - an internal combustion engine.
HEV (Hybrid EV) - uses a combination of an electric power plant (electric motor) and a power plant using a different type of fuel (for example, a gasoline ICE) in different forms of interaction:
1. Parallel hybrids - the electric motor and the ICE (as an option) are connected to transmission, and can work simultaneously.
2. Series hybrids - only the electric motor is connected to the transmission, the gasoline engine is used to power the electric motor, or recharge the batteries.
You can find another name for this type - E-REV or ER-EV (Extended Range EV), i.e. EVs with possibility of increasing the power reserve.
3. Power-split hybrids - a combination of two above. This type is used by most hybrid cars Ford, Lexus, Nissan.
Hybrid electric cars are divided by the degree of hybridization:
1. Full hybrid (full hybrid) - can be used to move both individually electric motor or gasoline engine, or a combination of both.
2. Mild hybrid (incomplete hybrid) - car cannot be moved with the help of only an electric motor.
Plug in (prefix "P") indicates that the vehicle’s rechargeable batteries can be recharged from an external power source. Acronyms PHEV (Plug in Hybrid EV), PEV (Plug in EV), etc.
For the supply of EV, different sources can occur - solar panels, hydrogen batteries, etc.

BEV (Battery EV) - a vehicle powered by rechargeable batteries. A vehicle that uses an electric power plant (electric motor) to carry out its movement, the power source of which is a purely rechargeable battery. An example is the Nissan Leaf.
FCEV (Fuel Cell EV) - a hydrogen-powered vehicle. A vehicle that uses an electric power plant (electric motor) for the movement to be carried out using hydrogen power sources. Electricity is generated by the interaction of hydrogen from hydrogen elements and oxygen from the environment.
GUEST BOOK
Electric, Hybrid, Hydrogen, Solar Car & Motorcycle Manuals, Brochures PDF; Specs, History


